Evaluating the Impact of Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibilities (CSR) Initiatives on Corporation’s Financial Performance and Brand Repuration
Introduction
Over the years, the significant of CSR in improving the financial performance and reputation of a company has increasingly gain interest in the field of corporate governance. This relevancy was sparked by the increase understanding of the impact of social responsibility among stakeholders, investors, and consumers. As a result, various companies are currently implementing CSR practices into their business technique as a means of enhancing their reputation, build brand trust, and increase financial performance. In view of this, Aggarwal (2016) posited that corporate social responsibility is gradually gaining attention in the corporate world as company seeks to find a balance between their financial objectives and their commitment to ethical, social, and environmental responsibilities. CSR encompasses variety of activities ranging from subscription to charity to sustainable business operations, and has been established to have an enormous impact on a company’s reputation and financial performance (Anand and Sharma, 2018).
Given the increasing awareness on the significance and impact of CSR for companies and businesses, various groups such as stakeholders, investors and consumers are becoming more insistent that companies act as reasonable members of society by utilizing their powers and assets to create a notable contribution to both society and the surrounding. To this effect, CSR has emerged as a fundamental factor in ensuring the building and stability of a company’s reputation. A brand with a strong reputation offering high quality of products and services stands a chance to allure and retain clients, including investors and competent employees. CSR has the potential to make this goal achievable by improving the company reputation though its commitment to ethical, social, and environmental responsibilities that are fundamental to its stakeholders. For instance, a company dedicated to minimizing greenhouse gases (GHGs) emission or fosters social justice is more likely to gain favorable response than ones that acts contrary to these principles.
Aside from its impact on brand reputation, CSR has played a crucial role in enhancing the financial performance of a company. Numerous studies reveal that there is a positive interaction between CSR and financial performance. This positive interaction is manifested in improving company sales, increased profits, and stock performance. In view of this, CSR helps to maximize a company’s profits, enhanced quality of service, and strengthen customer’s trust. Despite the connection between CSR and financial performance, it is very difficult to navigate the puzzle between these two concepts. As a result, there are various that can shape the outcome or success of CSR performance. For instance, companies viewed as “greenwashing” or involved in conducting superficial CSR operations without a sincere commitment can cause great damage to their reputation and financial performance.
However, companies face a major challenge in integrating CSR practices, especially in evaluating the role of their operations on brand reputation and financial performance. Even though there is an increase interest on this topic; some scholars does not approve the methodology employed in evaluating the role of CSR in enhancing a company’s financial performance. Various studies have proposed a method such as Key performance indicators or finance metrics to examine and evaluate the financial growth of a company. Example of finance metrics includes return on equity, earnings per share (EPS), and return on investment (ROI). Despite its impact, some scholars still present a contrary view contending that such metrics lacks the nitty gritty or rudiment to track the entire record of a company financial performance such as boosting an employee’s ability to perform a tasks effectively, minimizing the effect of ecosystem, and strengthening an organizational relationship with the community (Bhamra and Sondhi, 2017). Furthermore, stakeholder participation plays a crucial role in enhancing the role of CSR in boosting a company’s reputation and financial performance.
Some scholars are of the opinion that stakeholder engagement is an essential component of CSR and can enhance brand reputation (Albuquerque et al., 2018). Other scholars are of the opinion that in some cases, stakeholder engagement is irrelevant and may even damage a company’s financial performance (Cuong, 2023). Even though there is an ongoing debate, majority of scholars are well grounded with the belief that CSR had the potential to enhance the reputation and financial performance of a country. For instance, research shows that companies who invest in the practice of CSR will gain employee trust and loyalty; create a positive impression about the company, and a health financial record.
In furtherance, companies that incorporate the practice of CSR as their core values and objective are view as company with high standard of values, and committed to consumer preferences stands the chances of attracting customers to purchase their products and boost consumer’s loyalty and respect for the company. In essence, assessing the impact of CSR in enhancing a company’s reputation and financial performance is complex and involves breadth of topic. In this exploration, this study focuses on examining various factors that influence the performance of CSR efforts. By so doing, companies can establish and implement more efficient CSR practices fosters a healthy brand reputation and gain long-lasting financial success.
The Concept of Corporate Social Responsibilities, It benefits, and Impacts on Brand Reputation
The term Corporate Social Responsibilities is defined as where a company or an organization acknowledges and take responsibility on how their activities and operations affects the society and environment with the ultimate aim of making a beneficial impact on both society and environment (Dahlsrud, 2018). It is self-driven efforts that outdo adhering to law and regulations rather it focuses on contributing positive social, environmental, and economic impacts through the operation of the company.
CSR provides a broad range of services including ethical business practices, environmental sustainability, community participation, philanthropy, employee welfare, and safeguarding of human rights. The aim of CSR is to make an impact for sustainable development and create an equal value for all stakeholders including shareholders, customers, employees, suppliers, communities, and the environment (Maignan et al., 2019). Companies that have incorporated CSR practices may implement a variety of strategies and initiatives to accomplish their objectives such as implementing eco-friendly sustainable practice, donating a share of their profits to charitable organization, participating in voluntary movements, advocating for inclusion and diversity, and encouraging the need for education and training their workers (Porter and Kramer, 2016).
The notion of CSR has gained widespread recognition over the past few years, as consumers and investors are more and more demanding that companies take accountability to make a positive impact in their social and environmental responsibilities (Bhatt and Bhattacharya, 2018). Presently, many companies view CSR as a fundamental tool for developing their business strategies.
Highlighting the benefits of CSR, companies that employ CSR practices are more likely to gain attraction and favourable responses from the public, including consumers, stakeholders, and investors (Alexander and Buchholz, 2018). When companies decide to show commitment to social and environmental issues, they gain trust and reliability for their brand. As a result, consumers demonstrate trust in their products and recommend them to others, leading to positive word-of-mouth marketing. This in turn, heightened the company’s reputation and strengthens its relationship with consumers, leading to more business productivity. Simultaneously, increases the reputation of the company in the market, boosting sales performance and income. Consumers are more likely to show commitment to companies that commit to make positive impact to social and eco causes.
By implementing CSR operations, companies increase their brand loyalty and create a stronger bond with their consumers. Implementing CSR practices helps to reduce costs for business in the end. For example, adopting energy-saving practices helps to reduce the cost of utility bill, while waste reduction leads to reduction in disposal costs. CSR practice also helps to increase operational efficiency, lower the risks of supply chain, and encourages innovation, which can lead to cost reduction and boosts sales profits and revenue (Sen and Bhattacharya, 2020). On the other hand, employees who are confident of their employer’s dedication in implementing CSR practice tends to perform effectively, become active, and remain honest to the company. Accordingly, the company does not experience shortage of employees; this then minimizes the cost of hiring and training new employees.
Another benefits of implementing CSR is that it allow companies to gain easy access to emerging economy by showing a sense of dedication to social and environmental responsibilities, companies gain attraction from prospective audience (Vitezic, 2019). For instance companies that adopt sustainable practice (such as waste reduction) tends to appeal consumers who prioritize the importance of eco-friendly practice (protecting their environment). This helps to increase the sales revenue and profits of the company, create new business prospects, and increase the market portion of the company compared to its rivalries (Paul, 2019). In addition to this, companies that incorporate CSR practices are able to manage business hurdles/inefficiencies related to social and environmental cause. By implementing effective practice and communicating effectively with stakeholder, companies can minimize the costs of protecting their reputation from public damage, stay within the confines of the law, and maintain a good financial performance and success (Platnova, 2018).
Highlighting the role of CSR on brand reputation is important, as it significantly influence people perception of the company, which in turn, shapes how consumer behave, consumer choice of decision to purchase a product or service, and their loyalty to the brand (Muhammad, 2023). Brand reputation is important for all companies to thrive. Furthermore, CSR contributes significantly to the building and achieving an effective brand reputation. The impact of CSR on brand reputation manifest in various ways. Firstly, CSR enhances a company’s reputation by protecting a company that prioritizes sustainability practice from experiencing public criticism arising from environmental factors (Raza, 2020). This, in turn, creates a positive outlook of the company’s image and reduces the cost of legal suits or penalty. Secondly, CSR helps to distinguish a company from its opponents.
In a vast market, where products and services appears to be the same, a company’s dedication to create social and environmental impacts can distinguish them from other competitors (Saleh, 2013). They are more likely gained attraction from consumers who prioritizes the importance of ethical and sustainable practices, as a result increase brands trust. For instance, a consumer who prioritizes ethical trade practice may decide to work with a company that is dedicated to using ethically trade resources in its products different others who do not do so. Thirdly, CSR enables a company gain attraction from employees and help retain current employees from leaving. In today’s working environment, employees are ready to work with companies who have the same values with them and are dedicated to make a positive contribution (Vermeir, 2020). A company that is seen as socially accountable has the potential to draw and retain high skills professional, leading to increase productivity and the creation of new ideas. Furthermore, employees who believe in their company’s commitment to CSR practice are more likely to remain motivated and active in their duties (Ruf, 2021). This increase motivation and active participation can lead to high level of job satisfaction and reduces the chances of employee leaving the company.
Impact of CSR on Financial Performance
Indeed, CSR refers to the ability of a company to commit to making a positive contribution to the society by taking part in operations that goes beyond the fundamental business processes (Larran, et al., 2018). These operations include philanthropy, eco-friendly sustainable practice, social activities, and ethical business operation. Despite the fact that the role of CSR in enhancing the financial performance of a company cannot be easily analyzed, researchers have discovered that there is a correlation between CSR and financial performance.
With respects to the study conducted by Harvard Review Business, the study discovered that companies that are actively committed in executing CSR practice are open to excel in economic size and value, become more efficient with their net income or assets, and more efficient on their investment. This implies that clear link between CSR and a company’s financial performance. Also, the study found that companies with effective CSR practice stand a likelihood of attracting and keeping employees, leading to an overall good reputation.
In view of the study published in the Journal of Business observed that CSR has an advantageous influence on a company’s financial performance over a long period. In essence, companies that commits to the practice of CSR will experience a positive financial outcome. The study went further to examine data gathered from 130 companies and observed that companies who prioritizes CSR practice tend to have a high profits. These results were specifically evaluated by higher return of quality, return on assets, and return on investment. This shows that companies who invest in CSR activities will achieve a higher financial performance or greater profitability. In other words, a company’s strong financial performance depends on its involvement to CSR practice.
Nevertheless, it is crucial to point that the connection between CSR and financial performance is intricate, and the impact of CSR can differ based on the sector, the company’s capacity and resource, and the type of CSR practice being initiated. In furtherance to the above, the implementation of CSR activities is not only known for gaining positive financial performance. CSR activities can be implemented by a company for various factors including ethical cause or a intention to make create a unique contribution on the society.
In a nutshell, even though the correlation between CSR and financial performance does not have a clear path, there is a clear relevance that companies who engage in the business of executing CSR will experience a rapid growth in the financial status, especially in future time.
The Impact of Sustainability on Brand Reputation and Financial Performance
Sustainability has gained notable attention from companies over the years. It goes beyond been responsible to social concern but also serve as a yardstick in expanding the financial growth of a company. Companies that prioritize sustainability practice contribute to reducing the impact of ecosystem operations, build a positive impression for the brand where customers can trust and rely on the products and services offered by a company (Rui, 2023). By so doing, company can appeal the right consumers, investors, and stakeholder. Sustainable practice encompasses a wide variety of activities including ecosystem sustainability, recognizing and managing the overall impacts of a business on employee and customers and effective management of a company. Based on Harvard Business Review Study, companies that prioritize sustainable practice achieve a more pronounced result than their competitors in the long run.
The study examined 180 companies over 18years and discovered that those with active sustainability practice perform have a positive financial results in terms of higher return on assets and higher return on equity. Another study was conducted by MSCI ESG Research on the basis that companies with higher records in environmental, social, and governance are likely to experience reduction in costs of capital, which shows that investors will see such company as less risky, making it easy for them to borrow money.
Several companies across various sectors/industries have implemented a plan in executing sustainability practice. For example, Walmart has made remarkable advancement to minimize its GHG emission by employing natural resources such as wind power, and solar power to minimize waste. This approach has created a large impact in minimizing the influence of ecosystem in the operation of a company activity. Same thing applies to Unilever setting a goal to cut down on its environmental influence, such as minimizing the emission of gas from greenhouse and enhancing water management. Both companies have taken positive steps to improve their financial performance by investing on sustainable practice.
Companies express a sense of concern towards the expenses associated with the implementation of sustainability practice and how these practice would influence the profitability of a company. Given that financial performance is a company top priority in the course of implementing sustainable practice and adhering to the principles of SDGs’. Studies reveal that the implementation of Sustainable practice and the integration of SGDs enhance a company reputation, increased operational efficiency, lower expenses, improved new ideas, and ensure a better risk management, ultimately leading to a positive financial performance (Vorontsova et al., 2022).
Conversely, other studies have demonstrated that a negative connection exist between SP and financial performance, arguing that implementing SDGs requires a greater amount of investment and high level of operational costs, which could affect a company’s short-term profitability (Galant and Cadez, 2017).
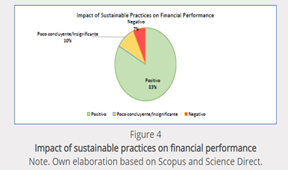
The analysis of financial outcome about companies’ dedication to the SDGs is a profound contribution to understanding how sustainable practices are demonstrated in financial performance. The above table shows a nuanced understanding of the relationship between sustainability and financial performance. The above analysis discovered that 83% shows that there is a correlation between sustainable practices and financial performance, while 10% shows an inconclusive relationship and 7% shows a negative relationship.
However, there is a growing awareness that companies who invest in sustainability practice can enhance their long-term market position, by managing the risks associated with the implementation of sustainability, promote creation of new ideas, and establish trust from investors and consumers who are deeply concern about social and environmental cause (Epstein, 2017). Companies that actively engaged in the implementation of sustainability practice has the ability to provide services and products at a lower opportunity cost than it trading competitors including creating a public impression about the company’s brand and attracting the right customers who are socially responsible (Chun, 2015). In conclusion, by engaging in sustainable practice, companies mitigate the effect of unexpected situation, provide quality service with little resources, identify and minimize waste to lower operational costs, create a positive impression about the company’s image and attract the potential customers.
Conclusion
Evaluating the impact of sustainability and CSR practice indicates a clear relevance on brand reputation and financial performance. It is a basic rule that companies, who are committed to implement sustainability and CSR practice experience greater profitability, save more and generates high revenue. We recommend that companies should endeavour to invest in sustainability and CSR practice as a means to improve their long-term goal. To optimize benefits, these practices should align with the company values and goals. Finally, we recommend that companies should regularly evaluate their financial and reputational performance of their sustainability and CSR practice to adjust and maximize over time.
References
Aggarwal, R. (2016). A study of the impact of corporate social responsibility on consumer buying behavior. Pacific Business Review International, 8(4), pp. 1-8.
Albuquerque, R., Koskinen, Y., & Zhang, C. (2018). Management of Science. Corporate Social Responsibility and Firm Risk: Theory and Empirical Evidence. Social Responsibility Journal 2 (7), pp. 831-852.
Alexander, G., & Buchholz, R. (1978). Corporate social responsibility and stock market performance.
Alexander, G., & Buchholz, R. (2018). Corporate social responsibility and stock market performance. Academy of Management Journal 7 (4), pp. 479-486.
Anand, M., & Sharma, P. (2018). Corporate social responsibility and firm performance: Empirical evidence from Indian firms. Journal of Cleaner Production, 203, pp. 1107- 1118.
Bhamra, H. S., & Sondhi, N. (2017). Corporate social responsibility and financial performance: Evidence from Indian firms. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 11(3), pp. 288-305.
Bhatt, P., & Bhattacharya, S. (2018). Corporate social responsibility and financial performance: An empirical study of Indian companies. Global Business Review, 19(2), pp. 455-468.
Carroll, A. B. (2019). The pyramid of corporate social responsibility: Toward the moral management of organizational stakeholders. Business horizons, 34(4), pp. 39- 48.
Chun, R. (2015). Corporate Reputation: Meaning and Corporate measurement reputation. International Journal of Management Reviews 6 (4), pp.91-109.
Cuong, D. P. (2023). The impact of sustainability practices on financial performance: empirical evidence from Sweden. Cogent Business & Management 4 (3), pp. 45-48.
Dahlsrud, A. (2018). How corporate social responsibility is defined: an analysis of 37 definitions. Corporate social responsibility and environmental management, 15(1), pp. 1- 13.
Epstein, M., Buhovac, A., Elkington, J., & Leonard, H. (2017). Making Sustainability Work: Best Practices in Managing and Measuring Corporate Social, Environmental, and Economic Impacts. Cognizance Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies, 7 (6), pp. 117-119.
Galant, A., & Cadez, S. (2017). Corporate social responsibility and financial performance relationship: A review of measurement approaches. Economic Research. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology 5 (4), pp. 553-557.
Larran, M., Martinez, I., & Martinez-Martinez, D. (2018). Relationship between corporate social responsibility and competitive performance in Spanish SMEs: Empirical evidence from a stakeholder’s perspective. International Journal of Entrepreneurship 3(1), pp. 64-73.
Maignan, I., Ferrell, O. C., & Ferrell, L. (2019). Corporate social responsibility and marketing: An integrative framework. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 33(1), pp. 3-18.
Muhammad, A. K. (2023). The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Financial Performance Mediated by Corporate Strategy, Corporate Reputation, Stakeholder Engagement & Political Connection. Cognizance Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies, 3 (7), pp. 279-292.
Paul, K. (2019). An Empirical Investigation of the Relationship between Change in Corporate Social Performance and Financial Performance: A Stakeholder Theory Perspective. Journal of Business Ethics, 8 (5), pp. 143-156
Platnova, E., Asutay, M., Dixon, R., & Mohammad, S. (2018). The impact of corporate social responsibility disclosure on financial performance: Evidence from the GCC Islamic banking sector. Journal of Business Ethics 1 (6), pp. 451-471.
Porter, M. E., & Kramer, M. R. (206). Strategy and society: The link between competitive advantage and corporate social responsibility. Harvard business review, 84(12), pp. 78-92.
Raza, A. (2020). Linking Corporate Social Responsibility to Customer Loyalty through Co-Creation and Customer Company Identification. Journal of Business Ethics, 8 (6), pp. 291-297.
Responsibility Journal, pp. 831-852
Responsibility Journal, pp. 831-852
Responsibility Journal, pp. 831-852
Responsibility Journal, pp. 831-852
Responsibility Journal, pp. 831-852
Responsibility Journal, pp. 831-852
Ruf, B., Muralidhar, K., Brown, R., Janney, J., & Paul, K. (2021). An Empirical Investigation of the Relationship between Change in Corporate Social Performance and Financial Performance: A Stakeholder Theory Perspective. Journal of Business Ethics 4 (3), pp. 143-156.
Rui, C. (2023). The impact of social responsibility on corporate financial performance: A systematic literature review. Available at: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/csr.2446> accessed on 3rd August, 2024.
Saleh, M., Zulkifli, N., & Muhammad, R. (2013). An Empirical Examination of the Relationship between Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure and Financial Performance in an Emerging Market. Public Administration & Management 3 (2), pp. 123-165.
Sen, S., & Bhattacharya, C. B. (2020). Does doing good always lead to doing better? Consumer reactions to corporate social responsibility. Journal of marketing research, 38(2), pp. 25-43.
Vermeir, W., & Corten, F. (2020). Corporate social responsibility and financial performance. Corporate Governance 5 (3), pp. 129-138.
Vitezic, N. (2016). Corporate Reputation and Social Responsibility: An Analysis of Large Companies in Croatia. International Business & Economics Research Journal (IBER), 8 (9), p. 85.






